What Is a Bridge Rectifier Module? Structure, Function, and Application

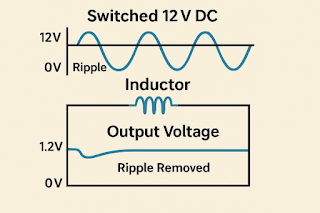
In a typical power supply circuit, the bridge rectifier plays a central role. It converts alternating current (AC) into direct current (DC), allowing stable and consistent power delivery to electronic components. In particular, the integrated bridge rectifier module simplifies circuit design by consolidating four diodes into a single package. 1. What Is an Integrated Bridge Rectifier? An integrated bridge rectifier module is a component that combines four diodes into one compact package. It features four terminals: two for AC input and two for DC output. The main advantage is its ease of use and reduced soldering points on the PCB. 2. Advantages of Using a Bridge Rectifier Module Compact Design: Reduces the area needed on the circuit board. Simplified Assembly: Easier soldering with fewer connections. Enhanced Reliability: Pre-tested components minimize errors. 3. Pinout and Structure Bridge rectifier modules usua...